Most USB Flash Drives that you plug in to a Windows PC are detected automatically by the system. Some may need to be formatted before you can start using them. Put simply, formatting makes sure that the operating system can interact with the device. Files can be saved, loaded, deleted or edited.
Formatting may also prove useful if the device doesn’t work properly anymore, e.g., when it is not detected by Windows, or when you want to start anew and erase all data on the drive.
Windows includes tool to format drives. It is an easy process, but I still get emails every now and then from users who seek guidance.
Formatting drives in Windows
Formatting adds a file system to a drive. You may have heard about FAT32 or NTFS. These file systems have rules in which they operate. FAT32 devices, for instance, support only files up to 4GB in size.
Formatting helps when a fully functional drive is not recognized by the Windows operating system. It can’t magically repair a defective USB Flash Drive on the other hand.
Windows’ built-in tool to Format drives and partitions supports different file systems. You may use it to change the name of the volume and also some other parameters.
There is also an advanced tool, called Disk Management, which can be used to partition drives and more. Last but not least, you may also format drives from the command prompt.
Using the basic Format tool in Windows
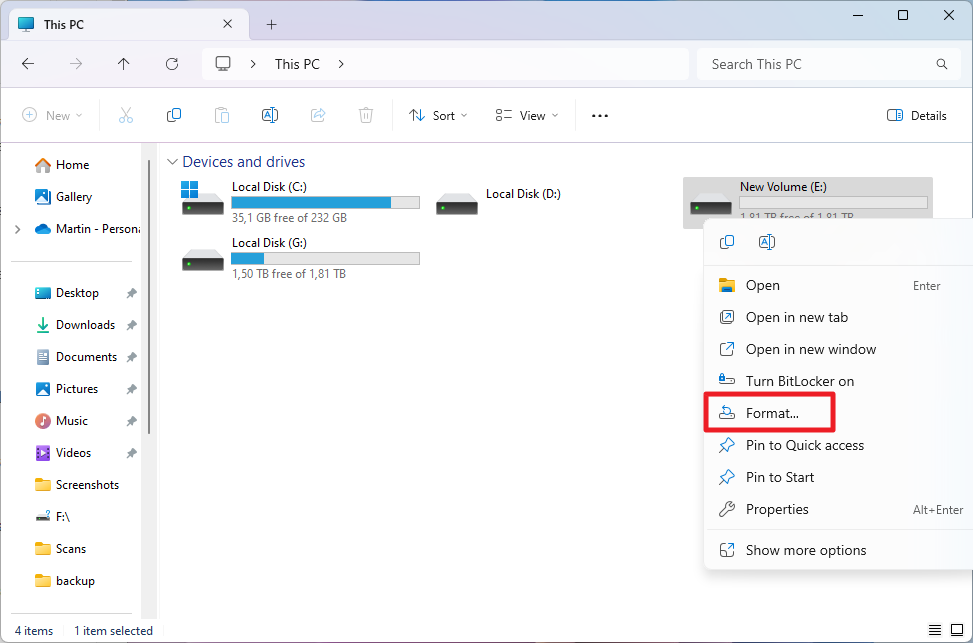
The easiest option to format a drive in Windows is to open File Explorer’s This PC overview. It lists all drives and volumes at the time.
Right-click on the drive that you want to format and select the Format option from the context menu. A small program opens.
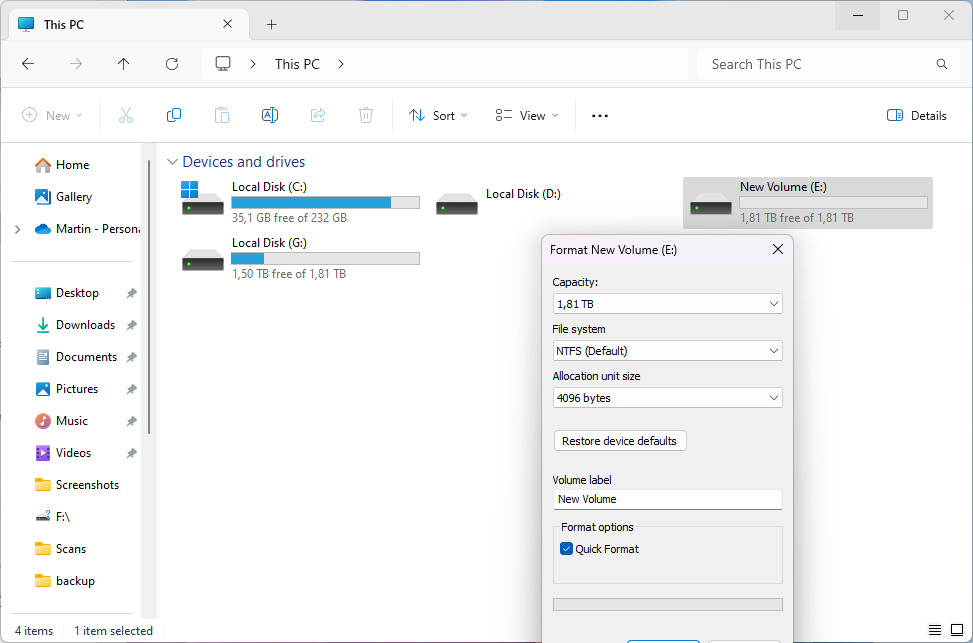
It lists the following information and options:
- The total capacity of the volume.
- The (new) File System. The three main file systems are FAT32, NTFS and exFAT. Windows does support additional file systems though.
- The Allocation unit size.
- A restore device defaults button.
- Volume Label field.
- Quick Format toggle.
Options may be limited here. Most users may want to keep the defaults. Quick format is the faster option, but it makes any file that is on the drive recoverable. If you want all files erased, uncheck the quick format option.
Note: to be 100% sure that no one can recover files on the drive, encrypt the entire drive before you run a full format.
Hit the Start button to start the process. Quick format should not take longer than a couple of seconds. Full format may take hours or even days. It depends on the size of the drive, its speed and also the load of the PC.
Disk Management, the advanced tool
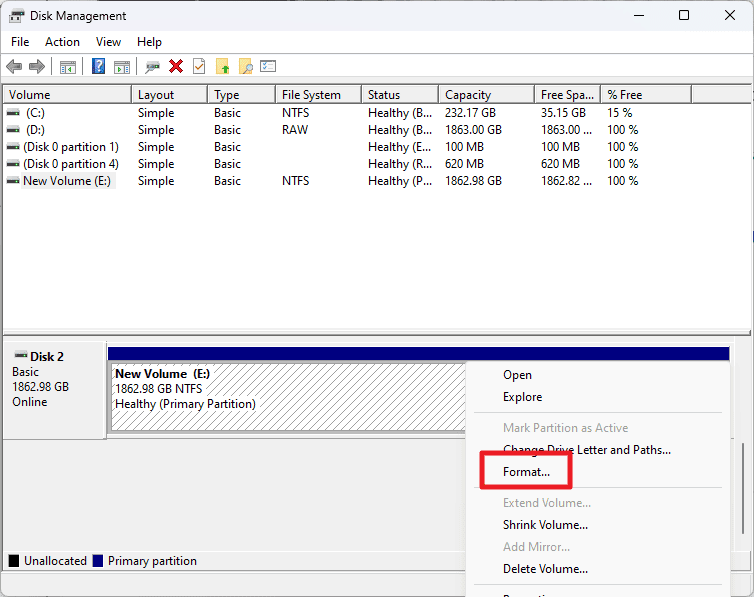
Disk Management is an advanced tool. It can be used to format drives, but also to create, delete, shrink or expand volumes, combine storage space and more.
The easiest way to start Disk Management on Windows is to use the keyboard shortcut Windows-X and select Disk Management from the menu that opens.
Windows displays all disks and their volumes on Start. Right-click on any volume and select the format option to format it. You will notice that the menu is different from the basic tool.
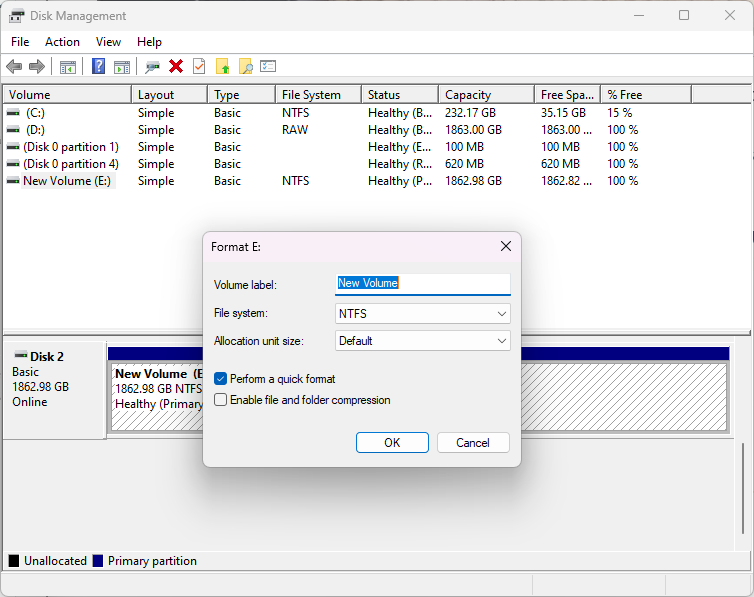
You get the same options, more or less, with one exception. You can enable file and folder compression to save storage space at the expense of performance.
Select OK to start the formatting of the selected volume.
Disk Management is helpful for advanced operations. You can split an external drive into two volumes, or merge volumes again. Right-click on all volumes and select “delete volume” to delete all existing volumes and create a single volume with all the available storage space.
Using the command line
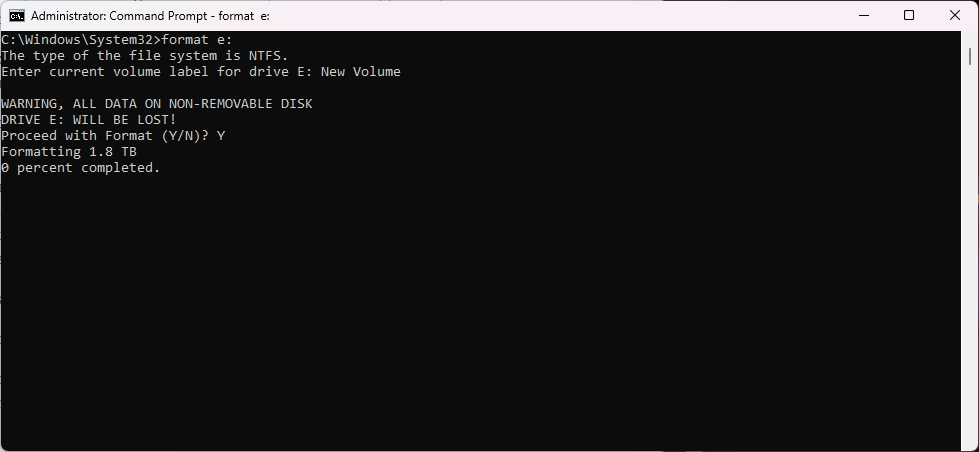
You may notice that the graphical user interface tools support only some or even just one file system. You may miss FAT32. If you need to assign a different file system to a drive, you may need to use the format tool from the command line.
To get started, open the Start Menu, type CMD, locate Command Prompt from the list of results and select run as administrators. Confirm the UAC prompt to continue.
You can run the command format /? to get a list of all parameters of the format command and some examples.
The base command is format drivelLetter, e.g., format e:. You are prompted to type the current label of the drive for confirmation. This is done to avoid accidental formats of other volumes. Windows displays a warning after you have typed the volume label correctly. All data on the specified volume is deleted when you proceed. Select Y to continue or N to cancel the operation.
Note that the default command runs a full format on the selected volume.
- The command format e: /q changes that, as it instructs Windows to run a quick format.
- The command format e: /q /fs:FAT32 defines the file system, in this case FAT32. You may also specify NTFS, which is the default, or exFAT instead.
The post How to format USB Flash Drives in Windows appeared first on gHacks Technology News.
